What is Subscription Pricing?
Subscription pricing is a business model where customers pay a recurring fee at regular intervals—monthly, quarterly, or annually—to access a product or service. This model is prevalent in the SaaS (Software as a Service) industry, providing a continuous revenue stream for providers and flexibility for customers.
At its core, subscription pricing contrasts with traditional one-time purchase models. Instead of paying a single, often substantial, upfront cost, customers make smaller, more manageable payments over time. This approach not only lowers the barrier to entry for customers but also fosters ongoing relationships between the service provider and the customer, which can enhance customer loyalty and satisfaction.
The SaaS industry has widely adopted subscription pricing because it aligns with software services. SaaS products are typically cloud-based, allowing users to access the subscription-based software and its updates online. Subscription models complement this by providing regular income supporting continuous development, maintenance, and customer support.
In subscription pricing, the price points and structure can vary significantly depending on the service offered and the target market. We’ll cover many pricing models and take a deep dive into strategies, but the most common are:
- Flat-rate pricing: A single price for access to the entire service, often used for straightforward, uncomplicated offerings.
- Tiered pricing: Multiple pricing levels, each with a different set of features or usage limits, catering to different customer segments and needs.
- Usage-based pricing: Charges are based on the extent of service usage, appealing to customers who prefer to pay only for what they use.
- Per-user pricing: Charges based on the number of users or seats, suitable for team-oriented or collaborative software.
Effective subscription pricing not only covers the cost of providing the service but also drives growth and profitability. It requires careful consideration of market demand, customer value perception, competitive landscape, and financial objectives. The right pricing strategy can enhance customer acquisition, retention, and overall revenue, making it a critical aspect of SaaS business models.
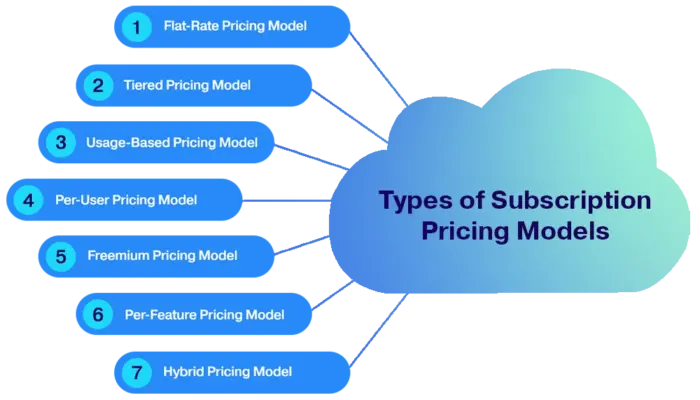
Types of Subscription Pricing Models
Subscription types are diverse, each designed to cater to different customer needs and business objectives. Choosing the right model can significantly impact a SaaS company’s ability to attract and retain customers while optimizing revenue. Here are some of the most common subscription pricing models used in the B2B industry:
1. Flat-Rate Pricing Model
Flat-rate pricing involves charging a single, consistent fee for access to the entire service. This model is straightforward and easy for customers to understand. It is ideal for services that offer a unified set of features without much variation in usage. Flat-rate pricing simplifies subscription-based billing and can be attractive to customers who prefer predictable costs.
Example: A project management tool that offers a full suite of features for a fixed monthly fee.
2. Tiered Pricing Model
Tiered pricing or Tiered Subscription Model offers multiple pricing levels, each with a distinct set of features or usage limits. This model caters to different customer segments by providing options that match varying needs and budgets. Tiered pricing allows businesses to capture a broader market and upsell customers to higher subscription tiers as their needs grow.
Example: A CRM platform that provides basic features at a lower tier, advanced analytics and automation at a mid-tier, and enterprise-level features at a premium tier.
3. Usage-Based Pricing Model
Usage-based pricing, also known as pay-as-you-go pricing or pay-per-use model, charges customers based on their actual usage of the service. This model is particularly appealing to customers who want to align their costs with their consumption. It is suitable for services where usage can vary significantly among customers.
Example: A cloud storage service that charges based on the amount of data stored and transferred.
4. Per-User Pricing Model
Per-user pricing or membership pricing model, charges customers based on the number of users or seats that access the service. This model is common for collaboration and team-oriented software, making it easy to scale costs with the size of the team using the service.
Example: A team communication tool that charges a fee for each active user per month.
5. Freemium Pricing Model
Freemium pricing offers a basic version of the service for free, with the option to upgrade to a paid plan for additional features or capabilities. This model helps attract a large user base and allows customers to experience the value of the service before committing to a paid plan.
Example: A note-taking app that offers essential features for free and charges for premium features like advanced search and collaboration tools.
6. Per-Feature Pricing Model
Per-feature pricing allows customers to pay for specific features they need, rather than a bundle of features. This model provides flexibility and customization, enabling customers to tailor the service to their precise requirements.
Example: An email marketing platform that offers core email-sending functionality at a base price package, with additional fees for advanced features like automation and detailed analytics.
7. Hybrid Pricing Model
Hybrid pricing combines elements of different pricing models to create a customized approach that meets the unique needs of both the business and its customers. This model can provide the best of multiple worlds, such as combining tiered pricing with usage-based pricing to accommodate different customer usage patterns.
Example: A video conferencing service that charges a base fee for a set number of users and adds usage-based fees for additional features like extra storage or high-definition video.

Benefits & Challenges of Subscription Pricing
Benefits:
Subscription pricing offers a myriad of advantages for both SaaS providers and customers. This model has become a cornerstone of the SaaS industry due to its ability to foster long-term customer relationships, generate predictable revenue, and provide continuous value. Here are some key benefits of subscription pricing:
Predictable Revenue Stream
One of the most significant benefits of subscription pricing for SaaS providers is the ability to generate a predictable and recurring revenue stream. This model allows companies to forecast their income more accurately, which aids in financial planning, resource allocation, and investment decisions. Predictable revenue helps stabilize the business and reduces the risks associated with fluctuating sales cycles.
Enhanced Customer Relationships
Subscription pricing fosters ongoing relationships between the provider and the customer. Unlike one-time purchase models, where interactions may be limited to the point of sale, subscriptions necessitate continuous engagement. Regular interactions for billing, support, updates, and renewals create opportunities to build stronger, more meaningful relationships, enhancing customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Lower Customer Acquisition Costs
The recurring nature of subscription payments often translates to lower initial costs for customers compared to one-time purchases. This lower barrier to entry can attract a broader customer base and reduce customer acquisition costs. Additionally, satisfied customers are more likely to renew their subscriptions and refer others, further driving growth through word-of-mouth and network effects.
Scalability and Flexibility
Subscription pricing models, especially tiered and usage-based pricing, offer scalability and flexibility. As customers’ needs evolve, they can easily upgrade or downgrade their plans. This flexibility ensures that customers are always on a plan that matches their current requirements, which can improve customer retention and lifetime value.
Continuous Improvement and Innovation
The recurring revenue generated by subscription models supports continuous improvement and innovation. SaaS providers can invest in regular updates, new features, and enhanced services without worrying about securing new sales for each upgrade. This continuous development cycle keeps the product competitive and aligned with customer needs, further boosting satisfaction and retention.
Better Customer Insights
Subscription pricing provides valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences. By analyzing subscription data, SaaS providers can identify usage patterns, popular features, and potential churn risks. These insights enable data-driven decision-making for product development, marketing strategies, and customer support initiatives, leading to more personalized and effective customer experiences.
Reduced Churn and Increased Retention
Well-structured subscription models can reduce customer churn and increase retention. By offering value continuously and maintaining regular contact with customers, providers can address issues proactively and keep customers engaged. Loyalty programs, personalized offers, and timely support can further enhance retention efforts, ensuring long-term customer relationships.
Improved Cash Flow Management
Subscription payments, typically collected monthly or annually, provide a steady inflow of cash, which aids in cash flow management. This consistency allows SaaS companies to manage their operational expenses, invest in growth initiatives, and respond to market changes with greater financial stability.
Cost Efficiency for Customers
For customers, subscription pricing often translates to cost efficiency. Instead of a large upfront investment, customers can spread their payments over time, making it easier to manage budgets. Additionally, customers benefit from regular updates and improvements included in their subscriptions, ensuring they always have access to the latest features without additional costs.
Enhanced Competitive Advantage
In a competitive market, subscription pricing can provide a significant advantage. Offering flexible and customer-centric pricing models can differentiate a SaaS product from competitors. The ability to adapt pricing to different customer segments and needs can attract a diverse customer base and position the product as a versatile and valuable solution.
Challenges:
While subscription pricing offers numerous benefits, it also comes with a set of challenges that SaaS providers must navigate to ensure success. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for maintaining a sustainable and profitable subscription-based business model. Here are some of the key challenges associated with subscription pricing:
Managing Churn
Customer churn, or the rate at which customers cancel their subscriptions, is a significant challenge for subscription-based businesses. High churn rates can erode revenue and offset the benefits of acquiring new customers. To mitigate churn, SaaS providers must focus on delivering consistent value, maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction, and implementing effective retention strategies. Regularly analyzing churn data to identify patterns and reasons for cancellations is essential for addressing the underlying issues.
Pricing Strategy Complexity
Developing an effective subscription pricing strategy can be complex. Providers must balance the need to attract new customers with the need to generate sufficient revenue. Pricing too high can deter potential customers, while pricing too low can undermine profitability. Additionally, determining the right mix of features and pricing tiers requires a deep understanding of customer needs and market dynamics. Frequent pricing adjustments may be necessary to stay competitive and meet evolving customer expectations.
Revenue Recognition and Accounting
Subscription-based revenue models require careful revenue recognition and accounting practices. Unlike one-time sales, subscription payments are typically recognized over the duration of the subscription period. This can complicate financial reporting and necessitate sophisticated accounting systems to ensure compliance with relevant standards, such as ASC 606 or IFRS 15. Accurate revenue recognition is critical for maintaining financial transparency and making informed business decisions.
Customer Acquisition and Retention Costs
While subscription pricing can lower initial customer acquisition costs, maintaining a steady stream of new customers and retaining existing ones requires ongoing investment. Marketing, sales, and customer support efforts must be sustained to attract and retain subscribers. Balancing these costs with the recurring revenue generated is crucial for achieving profitability. Additionally, providing continuous value through product updates and enhancements can incur significant expenses.
Handling Diverse Customer Needs
Subscription pricing models, especially those with multiple tiers, must cater to a diverse range of customer needs and preferences. Creating a pricing structure that appeals to various customer segments without causing confusion or dissatisfaction can be challenging. Providers need to ensure that each tier offers clear and compelling value, making it easy for customers to choose the plan that best suits their requirements. Regularly gathering customer feedback and monitoring usage patterns can help refine pricing strategies.
Competitive Pressure
The SaaS market is highly competitive, with new entrants and existing players continuously vying for market share. Competitive pressure can lead to price wars, where providers are compelled to lower their prices to remain attractive. This can erode margins and make it difficult to sustain profitability. Differentiating through unique features, superior customer service, and innovative pricing models is essential for standing out in a crowded market.
Customer Expectations and Service Quality
Subscription models create ongoing relationships between providers and customers, raising expectations for consistent service quality and continuous improvement. Meeting these expectations requires robust infrastructure, responsive customer support, and regular product updates. Failing to deliver high-quality service can lead to dissatisfaction and increased churn. Providers must invest in technology, talent, and processes to ensure a seamless and positive customer experience.
Pricing Transparency and Communication
Transparent and effective communication of pricing and plan details is critical for building trust with customers. Hidden fees, complex terms, or unclear value propositions can lead to confusion and frustration. Providers must ensure that their pricing is straightforward, well-communicated, and easily accessible. Clear documentation, user-friendly interfaces, and proactive customer education can help mitigate misunderstandings and enhance customer satisfaction.
Handling Subscription Cancellations and Refunds
Managing subscription cancellations and refund requests can be challenging, especially if policies are not clearly defined. Providers must establish fair and transparent cancellation and refund policies to maintain customer trust and minimize disputes. Automated processes for handling cancellations and prorated refunds can streamline operations and improve customer satisfaction.
Scaling and Infrastructure
As subscription businesses grow, they must ensure that their infrastructure can scale to accommodate an increasing number of customers. This includes maintaining system performance, data security, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Scaling operations efficiently while maintaining high service levels can be resource-intensive and requires careful planning and investment.
How to Choose the Right Pricing Model
Choosing the right pricing model for your SaaS business is a critical decision that can significantly impact customer acquisition, retention, and overall revenue. A well-structured pricing strategy aligns with your business goals and customer needs, fostering growth and profitability. Here are key considerations and steps to help you select the most suitable subscription pricing model:
Understand Your Customer Segments
Begin by identifying and understanding your different customer segments. Consider factors such as company size, industry, usage patterns, and budget constraints. Different segments may have unique needs and willingness to pay, which should influence your pricing strategy. Conduct market research, gather customer feedback, and analyze usage data to gain insights into your customer base.
Analyze Competitor Pricing
Examine the pricing strategies of your competitors to understand the market landscape. Identify the strengths and weaknesses of their approaches and look for gaps that your pricing model can fill. While it’s important to stay competitive, avoid the temptation to simply match competitors’ prices. Instead, focus on differentiating your offering and providing superior value.
Evaluate Your Value Proposition
Clearly define the value your product provides to customers. How does it solve their problems or improve their operations? A strong value proposition justifies your pricing and helps customers understand the benefits they will receive. Ensure that your pricing reflects the perceived value of your product, making it easier for customers to see the return on investment.
Align with Business Goals
Your pricing model should support your overall business goals, whether they involve rapid growth, market penetration, or maximizing profitability. For example, if your goal is to quickly grow your customer base, a freemium or low-cost entry-tier model might be effective. If profitability is the priority, focusing on higher-value tiers or usage-based pricing could be more suitable.
Test and Iterate
Implementing a pricing model is not a one-time decision. It’s crucial to test different approaches and iterate based on customer feedback and market response. Consider conducting A/B tests, offering limited-time promotions, or piloting new pricing tiers with a subset of customers. Monitor key metrics such as conversion rates, customer satisfaction, and churn to gauge the effectiveness of your pricing strategy.
Simplify Pricing Structure
While it’s important to offer options, avoid overly complicated pricing structures that can confuse customers. Aim for simplicity and clarity in your pricing tiers and feature sets. Customers should be able to quickly understand the differences between plans and identify the one that best meets their needs. Clear and transparent pricing builds trust and makes the purchasing decision easier.
Factor in Costs and Margins
Ensure that your pricing covers the costs of delivering the service and provides a healthy margin. Consider direct costs such as development, infrastructure, and customer support, as well as indirect costs like marketing and sales. Pricing too low can lead to unsustainable operations, while pricing too high can deter potential customers. Balance your pricing to achieve profitability while remaining attractive to your target market.
Address Potential Churn
Design your pricing model with customer retention in mind. Offer value at every pricing tier to keep customers engaged and satisfied. Consider providing incentives for longer-term commitments, such as discounts for annual subscriptions, to reduce churn. Regularly update and enhance your product to ensure that customers continue to perceive its value over time.
Ensure Flexibility and Scalability
Choose a pricing model that can evolve with your business and customer needs. As your product develops and your customer base grows, you may need to adjust your pricing strategy. Ensure that your model allows for scalability, whether through adding new tiers, adjusting usage limits, or introducing additional features.
Leverage Technology and Analytics
Utilize pricing software and analytics tools to gain insights into customer behavior, pricing performance, and market trends. These tools can help you make data-driven decisions and optimize your pricing strategy over time. Regularly review and adjust your pricing based on the insights gathered to ensure continued alignment with market dynamics and customer expectations.
Effective Pricing Strategies for SaaS
Implementing effective pricing strategies is crucial for SaaS companies to attract and retain customers, maximize revenue, and stay competitive. The right strategy can enhance customer satisfaction, optimize revenue streams, and support sustainable growth. Here are several effective SaaS pricing strategies that companies can employ:
1. Tiered Pricing Strategy
Description: Tiered pricing offers multiple pricing levels, each with a distinct set of features or usage limits.
Benefits:
- Appeals to different customer segments.
- Encourages customers to upgrade as their needs grow.
- Provides clear options for varying budgets.
Implementation: Clearly define the features and benefits of each tier. Ensure that higher tiers offer significant value to justify the increased cost. Use customer data to identify common usage patterns and tailor your tiers accordingly.
2. Usage-Based Pricing Strategy
Description: Usage-based pricing, or pay-as-you-go pricing, charges customers based on their actual usage of the service.
Benefits:
- Aligns costs with customer usage, making it attractive for cost-sensitive customers.
- Scales with the customer’s needs.
- Reduces barriers to entry for new customers.
Implementation: Ensure accurate and transparent tracking of usage. Set clear pricing metrics (e.g., per gigabyte, per user action). Provide customers with dashboards to help them monitor their consumption and anticipate costs.
3. Freemium Strategy
Description: The freemium strategy offers a basic version of the service for free, with the option to upgrade to a paid plan for additional features or capabilities.
Benefits:
- Attracts a large user base quickly.
- Allows customers to experience the product before committing to a paid plan.
- Creates opportunities to upsell paid plans.
Implementation: Ensure the free version provides genuine value but leaves room for customers to grow into paid plans. Highlight the benefits of upgrading through in-app messaging and email marketing. Monitor conversion rates from free to paid plans and optimize the upgrade path.
4. Per-User Pricing Strategy
Description: Per-user pricing charges customers based on the number of users or seats that access the service.
Benefits:
- Scales with the customer’s team size.
- Simple and easy to understand.
- Encourages growth within customer organizations.
Implementation: Offer volume discounts for larger teams to encourage scaling. Clearly communicate the value of adding more users, such as enhanced collaboration features. Regularly review user activity to ensure compliance with the pricing terms.
5. Value-Based Pricing Strategy
Description: Value-based pricing sets prices based on the perceived value of the product to the customer rather than on costs or competition.
Benefits:
- Maximizes revenue potential.
- Aligns pricing with customer willingness to pay.
- Enhances perceived value and differentiation.
Implementation: Conduct market research to understand customer pain points and the value they place on your solution. Communicate the unique benefits and ROI of your product. Be prepared to adjust pricing as customer needs and market conditions evolve.
6. Bundled Pricing Strategy
Description: Bundled pricing packages multiple features or products together at a discounted rate compared to purchasing each separately.
Benefits:
- Increases average revenue per user (ARPU).
- Simplifies the buying decision.
- Encourages adoption of multiple features or products.
Implementation: Identify complementary features or products that offer more value together. Ensure that bundles provide a clear financial benefit over individual purchases. Regularly review bundle performance and customer feedback to make adjustments.
7. Discount and Promotional Strategy
Description: Offering discounts and promotions, such as introductory pricing, seasonal discounts, or loyalty rewards, to incentivize new sign-ups and retain existing customers.
Benefits:
- Boosts customer acquisition and retention.
- Creates urgency and drives sales.
- Rewards loyal customers and reduces churn.
Implementation: Clearly define the terms and duration of discounts and promotions. Use limited-time offers to create urgency. Track the effectiveness of each promotion and adjust future campaigns based on performance data.
8. Subscription Discount Strategy
Description: Offering discounts for customers who commit to annual subscriptions instead of monthly payments.
Benefits:
- Increases cash flow and reduces churn.
- Provides financial stability and predictability.
- Encourages long-term customer relationships.
Implementation: Highlight the cost savings of annual plans in your pricing page and marketing materials. Offer additional benefits for annual subscribers, such as priority support or exclusive features. Monitor renewal rates and engage with customers before their subscriptions expire to encourage renewals.
9. Customized Pricing Strategy
Description: Providing customized pricing solutions for enterprise customers or those with unique needs.
Benefits:
- Accommodates large and complex customer requirements.
- Enhances customer relationships and satisfaction.
- Allows for higher pricing flexibility and potential revenue.
Implementation: Develop a scalable process for creating and managing custom pricing agreements. Train your sales team to identify opportunities for customized pricing and to negotiate effectively. Ensure that custom pricing solutions are aligned with your overall pricing strategy and business goals.
10. Market Penetration Pricing Strategy
Description: Setting a lower initial price to quickly gain market share and attract new customers, with plans to increase prices later.
Benefits:
- Rapidly builds a customer base.
- Increases brand awareness and market penetration.
- Establishes a foothold in competitive markets.
Implementation: Communicate the limited-time nature of the introductory pricing. Plan for a gradual price increase strategy to avoid customer backlash. Monitor market response and adjust pricing as needed to achieve long-term profitability.
SaaS Subscription Pricing in Action
Understanding how successful SaaS companies implement their subscription pricing models can provide valuable insights and inspiration for your strategy. Let’s explore three subscription pricing examples: Adobe Creative Cloud, AWS (Amazon Web Services), and Microsoft Office 365.
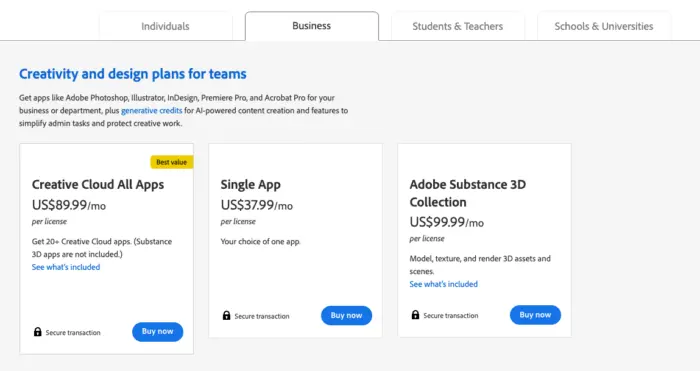
Adobe Creative Cloud
Overview: Adobe Creative Cloud offers a suite of creative applications and services for design, photography, video, and web development. Adobe uses a tiered pricing model to cater to individual users, teams, and enterprises.
Pricing Tiers:
- Individual Plans: Includes access to specific apps (e.g., Photoshop, Illustrator) or the entire suite. Options are available for monthly or annual commitments.
- Student and Teacher Plans: Provides discounts for students and educators on individual plans, making the software more accessible to the educational sector.
- Team Plans: Offers collaborative tools, additional storage, and advanced support, catering to small to medium-sized businesses.
- Enterprise Plans: Includes advanced features, customized licensing, enhanced security, and dedicated support, designed for large organizations and institutions.
Benefits: Adobe’s tiered pricing allows users to choose plans based on their specific needs and budget. The variety of options ensures that individuals, educational institutions, small businesses, and large enterprises can find a plan that fits their requirements. The clear differentiation between plans helps customers understand the benefits of upgrading.
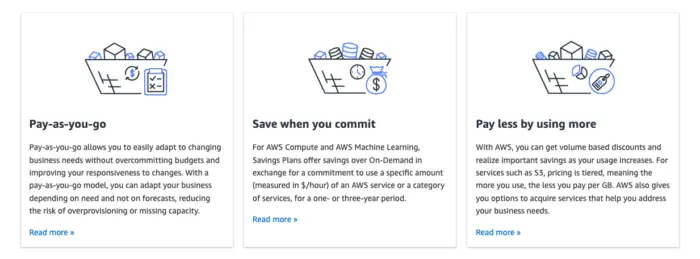
AWS (Amazon Web Services)
Overview: AWS offers a comprehensive suite of cloud computing services, including storage, compute power, databases, and more. AWS primarily employs a usage-based pricing model, charging customers based on their actual consumption of resources.
Pricing Structure:
- Pay-As-You-Go: Customers are billed based on their usage of services such as EC2 (compute), S3 (storage), and RDS (databases). This model provides flexibility and scalability.
- Reserved Instances: Offers discounts for customers who commit to using specific resources for a one- or three-year term, providing cost savings for predictable workloads.
- Free Tier: New customers receive a limited amount of free usage for certain services for the first 12 months, encouraging trial and adoption.
Benefits: AWS’s usage-based pricing aligns costs with actual consumption, making it attractive for startups, enterprises, and everything in between. The flexibility of pay-as-you-go subscription model and the cost savings of reserved instances cater to a wide range of customer needs and usage patterns. The free tier helps new customers get started without an initial financial commitment.
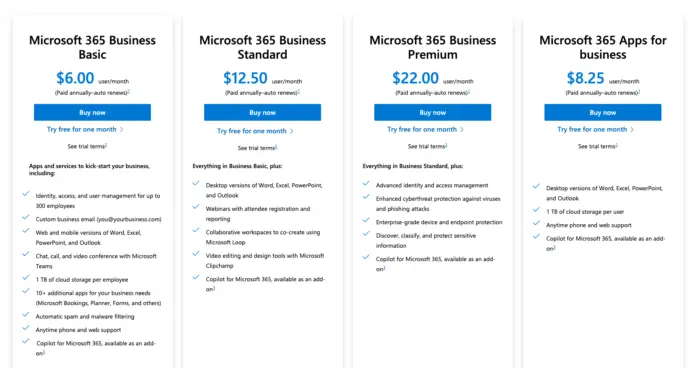
Microsoft 365
Overview: Microsoft 365 is a cloud-based suite of productivity tools, including Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and collaboration services like Teams and OneDrive. Microsoft 365 uses a subscription-based pricing model to offer individual, family, and business plans.
Pricing Tiers:
- Personal Plans: Includes access to 365 apps and cloud services for individual users, available on a monthly or annual basis.
- Family Plans: Offers the same features as personal plans but for multiple users within a household, providing shared access and cost savings.
- Business Plans: Tailored for small to large businesses, with options like Microsoft 365 Business Basic, Business Standard, and Business Premium, each offering varying levels of apps, services, and administrative tools.
- Enterprise Plans: Designed for large organizations, these plans provide advanced security, compliance features, and extensive collaboration tools.
Benefits: Microsoft’s subscription-based pricing allows users to access the latest versions of 365 apps and cloud services without a significant upfront investment. The variety of plans ensures that there is a suitable option for individuals, families, small businesses, and large enterprises. Regular updates and added features enhance the value of the subscriptions over time.
CloudBlue: Diverse Pricing Models

Final Thoughts
Mastering SaaS subscription pricing is a crucial aspect of optimizing your business’s revenue potential. By understanding the various subscription pricing models, you can select the one that aligns best with your business goals and customer needs.
While the benefits of subscription pricing are numerous, it’s essential to navigate the challenges with a strategic approach. Implementing effective pricing strategies tailored to your SaaS product will not only enhance monetization but also drive customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Remember, the right pricing model can make a significant difference in your overall success, so take the time to analyze, test, and refine your approach to achieve the best results.